My teaching philosophy is rooted in the belief that every learner is capable of growth when given the right support, environment, and opportunities. I view education not merely as the transmission of knowledge, but as the holistic development of students- intellectually, emotionally, socially, and morally. I strive to create a student-centred classroom where learners actively participate, collaborate, question, reflect, and construct their own understanding. My role as a teacher is that of a facilitator, mentor, and guide who nurtures curiosity and encourages lifelong learning.
What is a teaching philosophy?
A teaching philosophy is a written statement that explains a teacher’s beliefs, values, and practices about teaching and learning. It describes how a teacher thinks students learn best, why they teach in a certain way, and what goals they have for students.
It acts as a personal guide that shapes lesson planning, classroom management, assessment, and interaction with learners.
Key Points
- A teaching philosophy expresses your core beliefs about education.
- It explains how you teach, why you teach, and what you want students to achieve.
- It reflects your understanding of learners, learning process, and effective pedagogy.
- It includes your approach to classroom environment, teaching strategies, use of technology, values, and assessment.
- It is often used in B.Ed coursework, teacher portfolios, job interviews, and professional statements.
A teaching philosophy is a personal statement that outlines a teacher’s beliefs, values, goals, and instructional approaches, guiding their decisions and actions in the teaching-learning process.
Though specific beliefs are often unique in some way to the educator, teaching philosophies tend to include some common elements:
Concept of learning
Learning is a process of acquiring or modifying knowledge, skills, behaviors, or attitudes through experience, study, or practice, resulting in relatively permanent changes in the learner.
- Skinner: Learning is a change in behaviour through reinforcement
- Piaget: Learning occurs through cognitive development and adaptation
- Vygotsky: Learning happens in a social context with guidance (ZPD)
- Bruner: Learning is active and discovery-based
Today, learning is viewed as:
- Learner-centered
- Based on constructivism (active knowledge construction)
- Supported by technology
- Focused on critical thinking, collaboration, and real-life application
Concept of teaching
Teaching is a purposeful and systematic activity designed to facilitate learning, bring about desired changes in the learner’s behaviour, and help them acquire knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes.
- Dewey: Teaching is providing experiences that lead to growth
- Bruner: Teaching is scaffolding the learner’s discovery process
- Skinner: Teaching is arranging reinforcement for effective learning
Today, teaching is seen as:
- Progressivism
- Essentialism
- Constructivist → learning by doing and thinking
- Collaborative → peer learning and group work
- Technology-integrated → digital tools and smart teaching aids
- Perennialism
- Existentialism
- Social Reconstructionism
- Behaviorism
- Humanism
- Technology-Integrated
- Focused on critical thinking, creativity, and real-life problem-solving
Student goals
Student goals are targeted outcomes that guide students’ academic, social, emotional, and personal growth during the learning process.
Student goals can be:
- Academic → related to knowledge and performance
- Personal → related to behaviour, values, and identity
- Career-oriented → related to future aspirations
- Social and Emotional → related to communication, cooperation, and well-being
Setting goals helps students become self-directed, confident, and responsible learners.
Teaching Methods, Strategies and Techniques
Teaching Approaches: The overall philosophy, theory, or viewpoint behind teaching and learning. It answers: What do I believe about how students learn best?
Examples:
- Constructivist Approach
- Learner-Centred Approach
- Teacher-Centred Approach
- Behaviorist / Cognitive Approaches
- Inquiry-Based Approach
Represents: Theory & Guiding Principles
Teaching Methods: A planned overall format of instruction used to implement the approach. It answers: How will I organize teaching to achieve learning?
Examples:
- Lecture Method
- Project Method
- Discussion Method
- Demonstration Method
- Problem-Solving Method
- Experiential Learning
Represents: Structure of Teaching
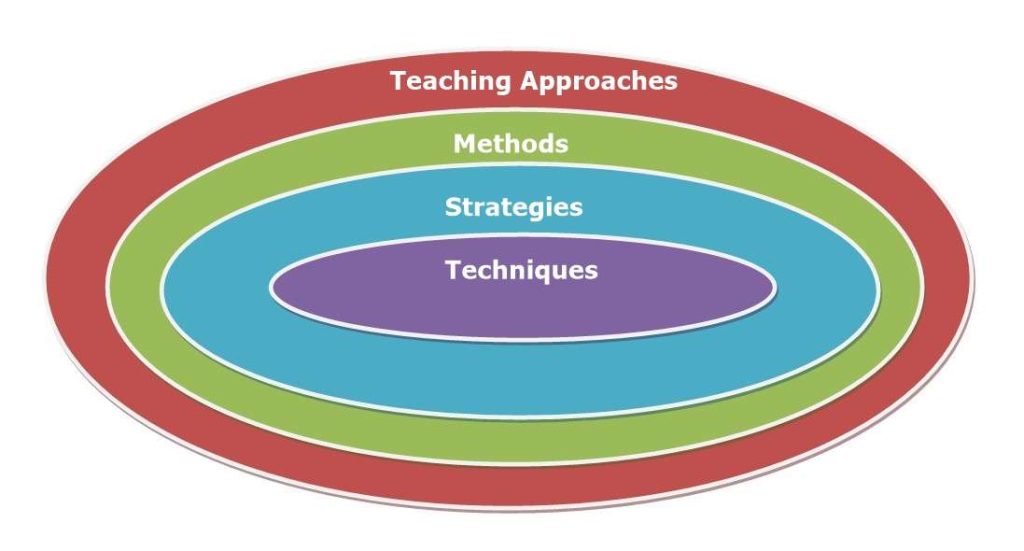
Teaching Strategies: Specific plans or techniques used within a method to achieve learning objectives. It answers: What plan will I follow within my method?
Examples:
- Cooperative Learning
- Brainstorming
- Scaffolding
- Differentiated Instruction
- Blended Learning
- Think-Pair-Share
Represents: Action Plan for Learning
Teaching Techniques: Small, practical classroom actions used to implement a strategy. It answers: What steps or actions will I use right now?
Examples:
- Using question prompts
- Giving reinforcement
- Using visual aids
- Note-making shortcuts
- Organizing group roles
Represents: Practical Skill / Micro-Level Tools
Teacher-student interactions
Teacher-student interactions are the communication, relationships, and exchanges between teachers and learners that support the teaching–learning process. These interactions include verbal and non-verbal communication, academic support, emotional encouragement, feedback, guidance, and classroom management.
Healthy and meaningful interactions create a positive learning environment, enhance motivation, and improve both academic and social development of students.
Teacher-student interaction refers to the communication and relationship between teachers and learners that facilitates academic learning and overall development.
Teacher–student interaction is crucial because it:
- Promotes active learning and participation
- Enhances motivation, confidence, and interest
- Improves academic achievement
- Develops social skills and emotional intelligence
- Builds a supportive classroom environment
- Helps teachers understand learners better
- Encourages a sense of belonging and trust
Assessment
Assessment is a systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting information about students’ learning progress, knowledge, skills, attitudes, and behavior. It helps teachers evaluate whether learning objectives are achieved and what improvements are needed. Simply, assessment is measuring learning to improve learning.
- Continuous process
- Based on evidence and observation
- Helps track academic and non-academic development
- Guides teaching methods and learner improvement
- Aligns with learning objectives and curriculum
Professional development
Professional development refers to continuous learning and improvement undertaken by teachers to enhance their knowledge, skills, attitudes, and professional competence throughout their career. It helps teachers stay updated with new teaching methods, technologies, curriculum changes, and educational research. It is a lifelong process that improves both teaching quality and student learning outcomes.
- Improve classroom teaching effectiveness
- Upgrade subject knowledge and pedagogical skills
- Support career growth and teacher confidence
- Adapt to educational reforms and innovations
- Promote reflective teaching and self-improvement
Similar:
- What Is a Teaching Philosophy? Examples and Prompts
- My Philosophy of Teaching
- Writing Your Teaching Philosophy
- The Most Common Teaching Philosophy Examples in 2025
- How to Craft Your Teaching Philosophy
Reference:
- “Publication Forum web site“. Retrieved 6 May 2018.
- “Teaching Philosophy website“. Retrieved 15 October 2018.
- AAPT website, Awards – Lenssen Prize Winners”. Retrieved 2 August 2014.